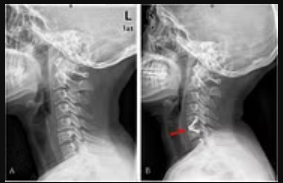
Awake spinal fusion is surgery conducted while the patient is awake, generally with a combination of local anesthesia and light sedation. This technique is used to reduce the complications of general anesthesia, including respiratory problems and recovery time. Surgeons are also able to obtain real-time feedback on nerve function through communication with the patient during the operation, potentially minimizing the risk of neurological injury. Recovery from awake spinal fusion may also be faster compared to traditional methods, with patients potentially experiencing less postoperative pain and a quicker return to their daily activities.
Căutare
Categorii
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jocuri
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Alte
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness
Citeste mai mult
Where else can gps tracker for car magnetic field be used?
GPS can be said to be an indispensable part of modern life, people's usual understanding of it is...
The Lifecycle and Sustainability of China Artificial Christmas Trees in the Recycling Industry
The recycling and reuse of China Artificial Christmas Trees have become a significant aspect of...
Kermit Camping Chair: A Must-Have for Every Outdoor Enthusiast
For those who love spending time in nature, comfort and convenience are essential. The Kermit...
Black OVO Hoodie: A Timeless Essential for Every Wardrobe
The Black OVO Hoodie is one of the most coveted pieces in streetwear fashion. A staple for many,...
Ваш успешный карьерный старт с нашим дипломом!
Диплом купить высшее образование. Получение высшего образования является важным этапом в жизни...